
Diffraction, however, can only be explained if the wave theory of light is taken into consideration.
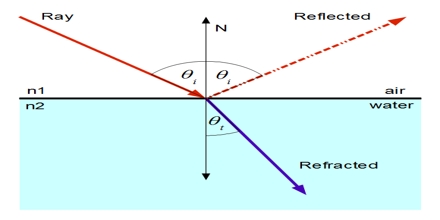
Interference occurs due to diffraction of light around the sides of the object, which causes the shadow to become fuzzy. This is apparent when you notice the fuzziness around the edges of the shadow.
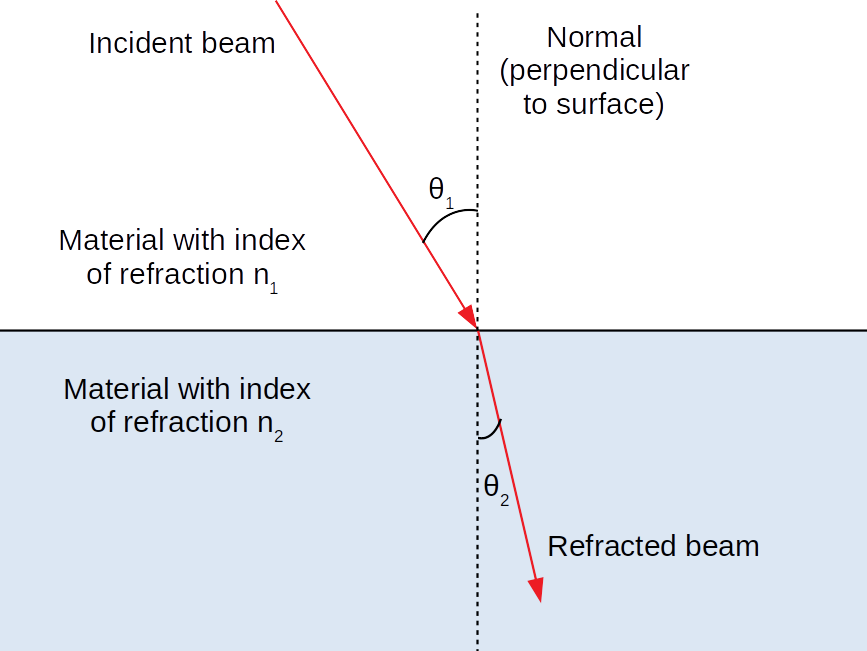
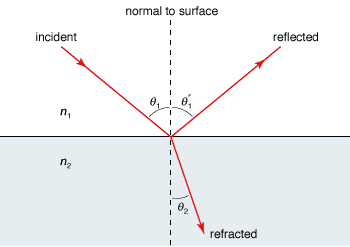
However light also displays the wave-like quality of diffraction. When light encounters an obstacle in its path, it tends to cause the formation of a shadow in the region behind the obstacle. Water waves and sound waves have the ability to travel around corners, obstacles and through openings, and light waves too are able to display this ability. This occurrence advocated its wave-like behavior because if light was just a stream of particles, how could it bend around the sharp boundaries of the slit and continue moving similar to a water wave? He used it to describe the phenomenon where a single beam of light, when passed through a narrow slit, was able to split into different directions creating an interference pattern. The term ‘diffraction’ was first coined in the year 1660, by Italian physicist Francesco Grimaldi. However, the discovery of diffraction of light proved that it had wave-like qualities as well. Many of light’s behavior and properties led to the conclusion that it must be a stream of particles. Diffractionįor many years, scientists had debated on whether light is a linear stream of particles or a wave. Where V1 and V2 represent the different velocities of light in each medium, and n1 and n2 represent the refractive index of each medium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
